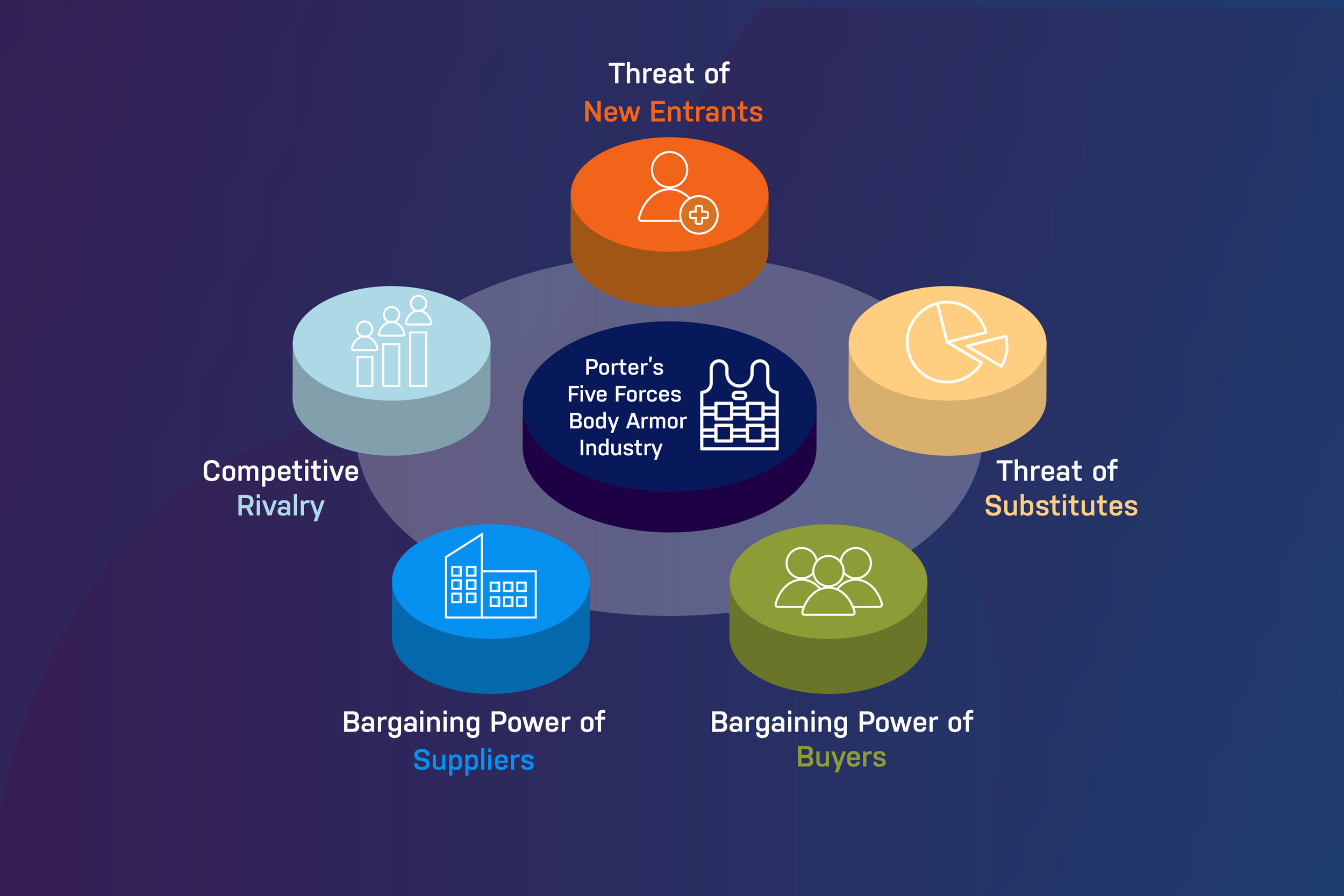
Porter's Five Forces in the Body Armor Industry
The body armor manufacturing industry, vital for law enforcement and military operations, presents a unique competitive landscape. Michael Porter's Five Forces framework, a tool for analyzing industry competitiveness and firm profitability since 1979, offers an insightful perspective into this sector's dynamics.
This article applies Porter’s Five Forces model to examine the body armor industry, delving into the threat of new entrants, bargaining power of suppliers and buyers, threat of substitutes, and competitive rivalry. Each force significantly influences the industry's market structure, strategic decision-making, and operational effectiveness, highlighting key factors that drive competition and profitability.
Threat of New Entrants in the Body Armor Industry
Barriers to entry in the body armor sector are notably high due to the industry's stringent technical requirements, rigorous regulatory standards, and substantial capital demands. This challenging environment naturally restricts market entry, favoring entities with significant resources and specialized expertise. Such barriers ensure that only well-prepared and resourceful players can successfully navigate the complexities of this industry.
Technical Expertise and Regulatory Compliance
The production of body armor requires advanced knowledge in design and engineering to comply with exacting safety standards, like those set by the National Institute of Justice (NIJ) in the U.S. This expertise isn't limited to product development but extends to consistent manufacturing adherence to these standards, reflecting the critical nature of body armor in life-saving scenarios.
Capital Intensity
Entering the body armor market demands considerable investment in manufacturing and research facilities. The use of high-cost materials such as advanced ceramics and ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene, along with the need for specialized machinery for production, escalates initial costs, posing a significant challenge for potential new entrants lacking substantial financial backing.
Advanced Technology and Systems
Continuous innovation is a hallmark of this industry, necessitating ongoing investment in research and development. As threats and material science evolve, manufacturers must adapt and invest in new technologies for product testing and development, representing a significant financial and technical commitment.
Market Niche Opportunities
Despite these barriers, niche markets offer opportunities for innovation and specialization. Emerging technologies, such as wearable electronics, and the need for body armor tailored to specific operational environments present potential entry points for startups and smaller firms capable of agile adaptation.
The body armor sector's high entry barriers, stemming from stringent technical requirements, regulatory standards, and significant capital demands, create an environment that favors well-resourced and expert entities. This market dynamic limits the entry of new players and sets the stage for the next critical aspect: the power of suppliers.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers
The bargaining power of suppliers plays a crucial role in shaping the body armor market, predominantly because of the reliance on specialized materials essential for crafting high-quality protective gear. This reliance impacts everything from cost structures to strategic decision-making and, ultimately, the profitability of manufacturers. The dynamic interplay between suppliers and manufacturers in this industry is critical in determining market trends and business success.
Dependence on Specialized Materials
The industry's reliance on materials like Kevlar and Dyneema, known for their ballistic resistance and durability, is critical. These high-performance fibers are essential due to their unique properties, offering limited alternatives. This dependence places manufacturers at the mercy of a few key suppliers, impacting supply chain stability and material availability.
Supplier Market Concentration
The market for these specialized materials is marked by a high concentration of a few suppliers. This small group's dominance in the market affords them considerable control over pricing and supply terms. The high costs associated with switching suppliers add to this power, making it challenging for manufacturers to negotiate more favorable terms or find alternative sources.
Impact on Costs and Profitability
The cost of materials like Kevlar and Dyneema forms a significant portion of the total production expenses in body armor manufacturing. Variations in the cost or availability of these materials directly impact the manufacturing cost structure, influencing the profitability of body armor manufacturers. This aspect becomes particularly crucial in environments where competitive bidding dictates cost-effectiveness.
Quality and Safety Standards Compliance
Suppliers also play a pivotal role in ensuring compliance with safety standards. The quality of input materials is a determining factor in both the certification and performance of the final body armor product, granting suppliers additional leverage in their relationships with manufacturers.
Strategic Partnerships and Vertical Integration
To mitigate the impact of supplier power, some body armor manufacturers might pursue strategies like forming strategic partnerships or vertical integration. Such approaches can offer more control over the supply chain, reduce dependence on external suppliers, and potentially lead to more stable material pricing and availability.
Suppliers hold significant sway in the body armor market due to the reliance on specialized materials essential for high-quality gear. This power influences manufacturers' cost structures, strategic decisions, and profitability. The industry's reliance on materials like Kevlar and Dyneema, crucial for their ballistic resistance and durability, underscores the importance of supplier relationships.
Bargaining Power of Buyers
The bargaining power of buyers, mainly law enforcement and military organizations, significantly dictates market dynamics in the body armor sector. This group's concentrated nature and high-stakes operational needs grant them substantial influence in the industry, shaping product specifications, pricing, and overall market trends. Their requirements and preferences are major driving forces in how body armor is developed and brought to market.
Concentration of Buyers and Market Influence
A small group of influential buyers distinctively influences the body armor market. Their high operational stakes necessitate body armor that adheres to stringent reliability and quality standards. This reliance on government and institutional buyers places them in a position to sway market dynamics, dictating terms to manufacturers significantly.
Customization and Quality Requirements
Buyers in this market often have unique requirements, leading to a need for customized body armor solutions. This demand for tailored products enables buyers to influence product design and manufacturing processes considerably. Such customization meets specific operational needs and strengthens the buyers' negotiation power.
Impact on Pricing and Profit Margins
The bargaining power of these concentrated buyers directly affects manufacturers' pricing strategies. In a market dominated by a few large buyers, manufacturers might face pressure to offer competitive pricing and enhanced features to win contracts, which could squeeze profit margins. This is particularly evident in scenarios where competitive bidding dictates contract awards.
Long-term Contracts and Dependence
Manufacturers often depend on long-term contracts with these buyers for stable revenue. However, this dependence heightens buyers' bargaining power, as losing a major contract to competitors can have significant business implications. This reliance further shifts the power balance towards the buyers.
Regulatory and Compliance Factors
Compliance with national and international standards is crucial for manufacturers to remain competitive, with buyers often setting these regulatory benchmarks. Meeting these stringent standards is vital for manufacturers to be considered viable suppliers, further empowering buyers in the industry.
Buyers, mainly law enforcement and military organizations in this sector, possess substantial bargaining power. Their influence shapes product specifications, pricing strategies, and overall market trends. The reliance on government and institutional buyers shifts our focus to the threat of alternative products.
Threat of Substitutes
While the body armor industry currently contends with a moderate threat from substitute products, this is primarily due to the exacting standards demanded by primary users like military and law enforcement agencies. Nonetheless, the landscape is evolving as ongoing advancements in technology and materials steadily reshape the prospects and potential impact of alternative protective solutions.
Current State of Substitute Products
Non-Traditional Protective Gear: The market has introduced alternatives like liquid armor, intelligent fabrics, and non-Newtonian fluid-based systems. Although these offer innovative protection mechanisms, they typically fall short of the ballistic protection levels provided by traditional body armor. Limited adoption of these substitutes is often due to concerns over their reliability, cost-effectiveness, and field-tested effectiveness.
Lightweight and Flexible Armor Alternatives: A growing trend is toward developing lighter and more flexible armor. These new solutions aim to match or exceed traditional armor's protection levels while reducing weight and bulk. However, before these alternatives can be widely adopted, they must undergo extensive testing and meet rigorous certification standards.
Innovations Leading to Potential Substitutes
Advancements in Material Science: The field of material science, especially in areas like nanotechnology, is on the brink of introducing new types of body armor. These innovations could offer enhanced ballistic protection, comfort, and excellent durability.
Integration of Technology: Incorporating wearable electronics, sensors, and connectivity into protective gear is poised to create advanced substitutes. These technologies could provide additional features such as health monitoring and communication capabilities, expanding the utility of traditional body armor.
Factors Influencing the Threat of Substitutes
Regulatory Standards and Certification: For any substitute product to be viable, it must adhere to stringent safety and performance standards. Achieving these certifications can be both time-consuming and expensive, potentially hindering the adoption of new substitute products.
Cost Considerations: The development and production costs of new protective technologies significantly affect their market entry. High costs could limit the adoption of these substitutes, especially if they are more expensive than existing solutions.
While the body armor industry faces a moderate threat from substitutes, ongoing technological and material advancements could alter this landscape. Innovations in material science and technology integration into protective gear are reshaping the potential of alternative solutions.
Competitive Rivalry
Competitive rivalry in the body armor industry is characterized by a moderate level of market concentration, with prominent players such as Point Blank Enterprises Inc., Safariland LLC, Avon Protection, Gentex Corp., and MKU Ltd., to name a few that are at the forefront. This competition is driven by various factors, from the drive for innovation and adherence to quality standards to the pursuit of government contracts and the reliance on government spending. These elements collectively shape the competitive dynamics, influencing how companies position themselves.
Market Concentration and Key Players
Dominant Firms: The market is primarily controlled by a few companies with significant market shares, reputations, and extensive product lines. Their established relationships with primary buyers further solidify their market positions.
Entry Barriers for New Competitors: The presence of these leading firms, coupled with the high entry barriers previously noted, curtails the entry of new competitors, contributing to the market's moderate concentration.
Factors Influencing Competitive Rivalry
Product Innovation: Innovation is a critical competitive factor in this industry. Companies continually develop lighter, more durable body armor to address evolving threats and operational needs. This innovation is a competitive edge and a necessity for survival and growth in the industry.
Quality and Reliability: Given the life-saving function of body armor, quality and reliability are paramount. Companies engage in intense competition based on these factors, with any compromise potentially having severe implications for users and manufacturers.
Government Contracts: A significant portion of revenue in this sector is derived from government contracts, which are typically large-scale and long-term. The fierce competition for these contracts is driven by their potential to provide stable revenue streams and strengthen market positions.
Impact of Government Spending
Budget Fluctuations: The industry’s reliance on government budgets means that defense and public safety spending changes directly affect market dynamics. Increases in spending generally intensify competition, while budget cuts can heighten competition due to a reduced market size.
Geopolitical and Policy Factors: Shifts in geopolitical scenarios, defense policies, and public safety priorities can alter demand, requiring companies to adjust their approaches and offerings strategically.
The industry's competitive rivalry, characterized by moderate market concentration, is dominated by key players like Point Blank Enterprises Inc., Safariland LLC, and Avon Protection. This rivalry, influenced by product innovation, quality standards, and government contracts, highlights the industry's dynamic nature.
The body armor industry, analyzed through Porter's Five Forces, reveals high entry barriers, significant supplier power, concentrated buyer influence, moderate substitute threats, and intense competitive rivalry.
IntelAlytic Strategic Recommendations
Firms should focus on innovation, quality, strong government relations, market intelligence, and supply chain management to navigate this complex landscape. These strategies are essential for firms to adapt to market dynamics, seize opportunities, and mitigate risks, ensuring sustained success in this critical sector.
Innovation and Diversification: Continuously innovate and diversify product offerings to stay ahead of technological advancements and changing market needs.
Quality and Reliability: Uphold the highest standards of quality and reliability, essential in an industry where products are critical for user safety.
Government Relations and Contracts: Develop and maintain strong relationships with government agencies. Stay informed on policy changes and public sector spending trends to align with future contract opportunities.
Market Intelligence: Invest in market intelligence to understand evolving threats and the operational needs of end-users, guiding product development and strategic positioning.
Supply Chain Management: Strengthen supply chain resilience through strategic partnerships, reducing dependency on single suppliers and mitigating risks associated with material shortages or price volatility.
Adhering to these strategies, firms in the body armor industry can effectively navigate complex market dynamics, seize opportunities, and mitigate risks, securing their place in a highly specialized and essential market.
Interested in working with IntelAlytic?
Explore IntelAlytic Services
Follow us on LinkedIn for daily tips and resources