The Strategic Impact of the Trade Agreements Act on Federal Procurement of Ballistic-Resistant Materials
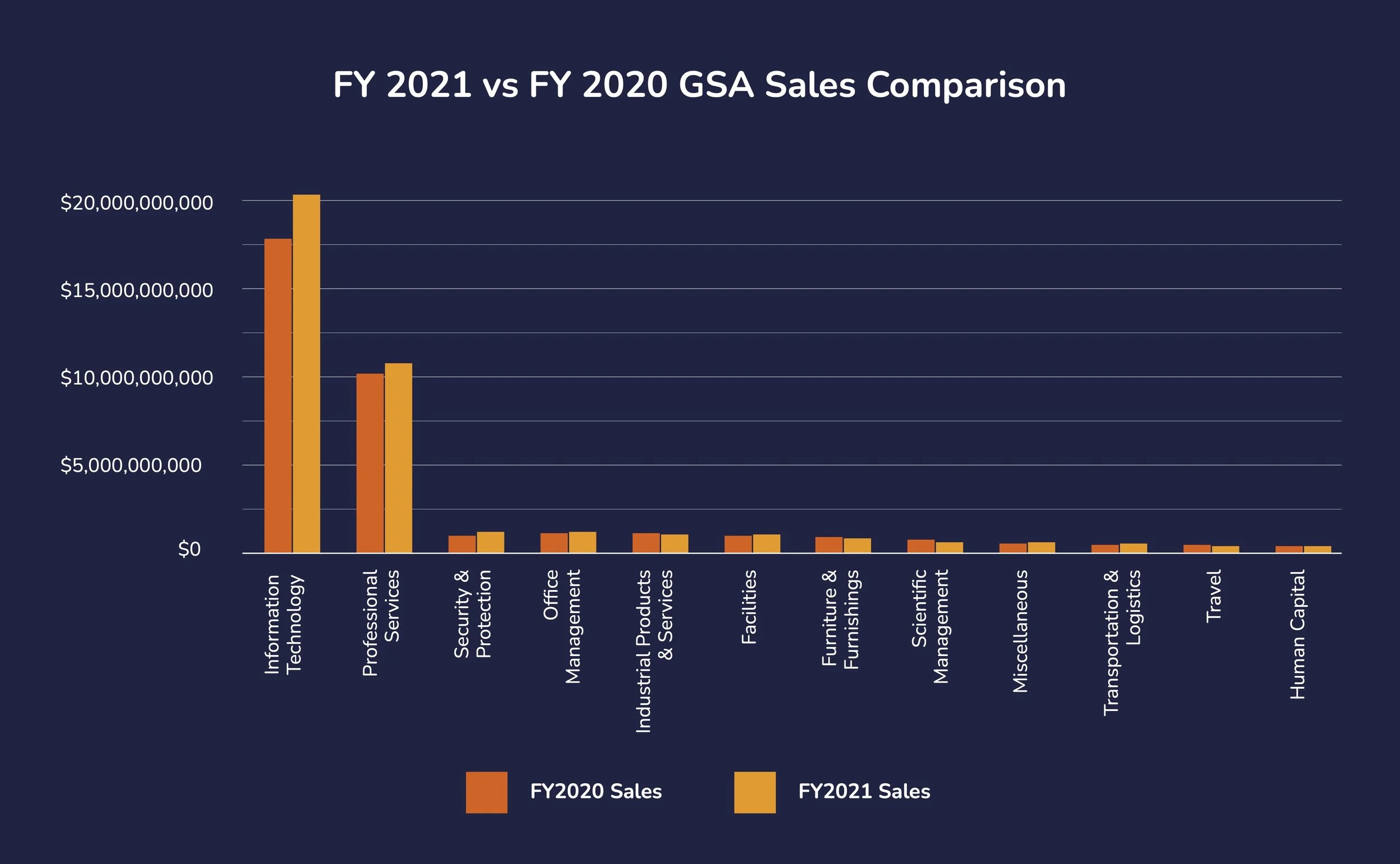
Did you know that in 2022 alone, the U.S. government spent over $9 billion on products through General Services Administration (GSA) Schedules? Amidst this substantial federal spending, understanding the Trade Agreements Act (TAA) is not merely beneficial—it's a gateway to a potentially lucrative market. The TAA sets stringent sourcing standards that directly influence the eligibility of products like ballistic-resistant materials used by military and law enforcement. By complying with these standards, vendors can position themselves for significant business opportunities.
This legislation defines how the U.S. government contracts with suppliers and ensures that these engagements adhere to broader international trade agreements. In this article, we delve deep into the nuances of the TAA, exploring how it affects the procurement of personal protection equipment and outlining the vital compliance requirements and strategic implications for suppliers. Failure to comply can mean missing out on a significant revenue stream and potentially facing severe legal consequences. It's crucial to understand these complex regulations to secure your success in federal contracting and avoid these potential pitfalls.
Navigating General Provisions and Waivers for Defense Products
The Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR) Subpart 25.4 delineates the extent of trade agreements that impact U.S. federal government acquisitions, including those relevant to military and law enforcement agencies. While international agreements like the World Trade Organization Government Procurement Agreement (WTO GPA) and various Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) foster the involvement of international suppliers, the procurement of defense-related items such as ballistic-resistant materials necessitates additional scrutiny due to their sensitive nature and critical importance to national security.
TAA Compliance Fundamentals
Understanding TAA Compliance
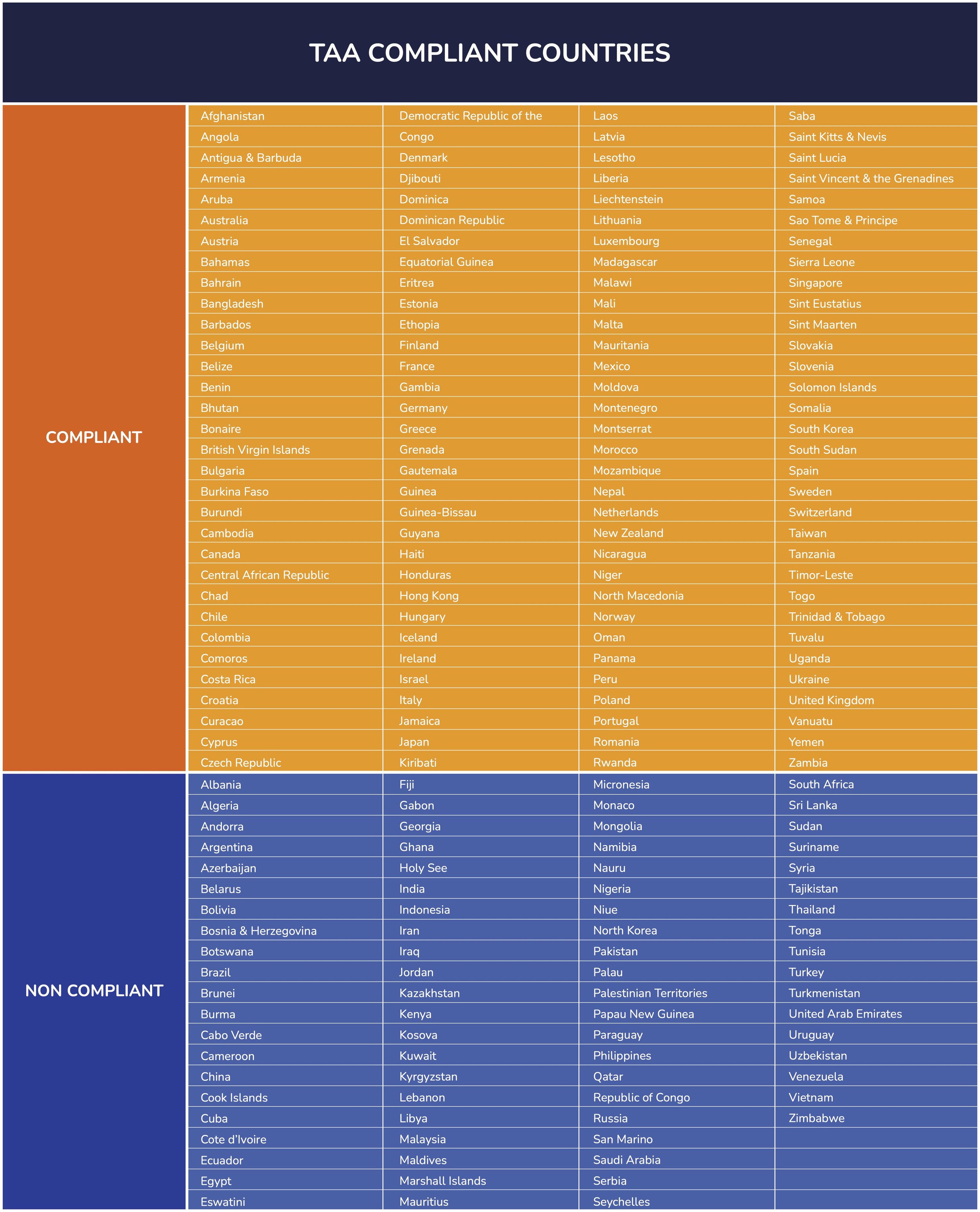
TAA compliance is not just a requirement but a crucial step for businesses wishing to sell their products to the U.S. government. Products must be manufactured in the United States or a TAA-designated country to be eligible for government contracts. This compliance ensures that U.S. trade agreements are honored and that the government procures goods from countries that adhere to these agreements, promoting fair and responsible trade practices essential for the integrity of the federal market.
The Trade Agreements Act of 1979 was established to foster fair competition within the global marketplace by requiring government procurements to prefer products from the U.S. or designated countries.
There are three categories of products under TAA compliance:
Domestic end products: Fully manufactured in the United States.
Designated country-end products: These are manufactured in a country with a trade agreement with the United States.
Foreign end products: Manufactured outside of the United States and not meeting the criteria for designated country end products.
2. Criteria for TAA Compliance
For a product to qualify under TAA, it must be made in the U.S. or undergo substantial transformation in the U.S. or a designated country. This transformation must significantly alter the product's form, fit, or function, demonstrating that the production or labor in the TAA-compliant country was substantial.
3. TAA Exceptions and Exclusions for Defense Articles
Crucial provisions within the TAA, as implemented through the FAR, outline specific exceptions that are pertinent to the procurement of defense and law enforcement equipment:
National Security Set-Asides: Procurements involving arms, ammunition, or war materials vital for national defense typically bypass standard international agreement requirements. This allows for the rapid and secure acquisition of essential defense materials, including ballistic-resistant products.
Exclusions under Individual Trade Agreements: Certain trade agreements include lists of excluded products and services tailored to meet participating countries' security policies and needs. For example, specific protective gear crucial for national security might be procured preferentially from domestic suppliers or trusted international sources despite broader trade agreements.
4. Waivers and Their Strategic Use
Under the TAA, the U.S. Trade Representative can waive the Buy American statute for eligible products from countries that have signed international trade agreements with the United States. For ballistic-resistant materials, such waivers allow the procurement of foreign-made goods when they meet required standards and no sufficient domestic alternatives are available. Understanding these waivers is essential for suppliers to navigate federal contracts effectively.
5. Understanding Procurement Thresholds and Procedures
The application of trade agreements to procure ballistic-resistant materials hinges on contract value thresholds detailed in the FAR. These thresholds dictate when international trade agreements are applicable and when acquisitions must rely solely on domestic or designated country sources. Adhering to procedural requirements, such as the equitable evaluation of foreign and domestic offers and the publicizing of contracts, is crucial to maintaining transparency and fairness in the procurement process.
6. Special Considerations for Developing and Beneficiary Countries
Initiatives like the Caribbean Basin Trade Initiative allow for the inclusion of ballistic-resistant materials from least-developed countries and beneficiary regions if these products meet safety and performance standards. By integrating these regions into the global supply chain, such policies support U.S. procurement needs and foster economic growth in these regions.
Leveraging GSA Schedules for Enhanced Federal Contracting in Ballistic-Resistant Materials
Integrating General Services Administration (GSA) Schedule Contracts is vital for vendors dealing with ballistic-resistant products. GSA Schedules simplify the process for businesses to sell products and services to the U.S. government, and TAA compliance is mandatory for items used by the military and law enforcement.
Key Features of GSA Schedules Relevant to Ballistic Materials:
TAA Designated Countries: Products must be manufactured or "substantially transformed" in the United States or one of the TAA-designated countries, ensuring adherence to high government procurement standards.
Compliance with Federal Acquisition Regulation: GSA contracts are governed by specific clauses in the FAR, such as FAR 52.225-5, which outline the TAA requirements. Vendors must familiarize themselves with these regulations to ensure compliance.
Product Categories and Specifications: Under GSA Schedules, ballistic-resistant materials fall within the "Security & Protection" category. Detailed specifications and federal standards for protection and durability must be met to ensure that the products provided are of the highest quality.
Maintaining TAA Compliance
Ensuring Continuous TAA Compliance: Actionable Insights and Common Pitfalls
Maintaining compliance with the Trade Agreements Act (TAA) is a regulatory requirement and a strategic advantage for businesses involved in federal contracting. To effectively navigate this landscape, businesses must adopt proactive strategies and be aware of common compliance pitfalls. Here are practical steps and critical mistakes to avoid:
Proactive Compliance Strategies:
Robust Supplier Vetting: Establish a rigorous vetting process for suppliers to ensure all components and materials are sourced from the U.S. or TAA-designated countries. Implement regular audits and require suppliers to certify the origin of their products.
Documentation and Record Keeping: Maintain meticulous records of each product's origin and transformation process. This documentation should be readily available for review in case of audits or compliance checks by government agencies.
Continuous Training and Updates: Ensure your procurement team is trained in the latest TAA requirements and updates. This includes understanding changes to the list of TAA-designated countries and any amendments to the Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR).
Integration of Compliance into Business Operations: Embed TAA compliance checks into your standard operating procedures. This should include regular compliance audits and reviews before finalizing contracts or introducing new products.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid:
Assuming Non-Change: One common mistake is assuming that once a product is compliant, no further checks are required. TAA compliance is dynamic; changes in manufacturing locations or supply chains can affect compliance status.
Overlooking Substantial Transformation Requirements: Misunderstanding or underestimating the requirement for substantial transformation is a frequent error. Ensure the transformation process significantly changes the product to meet the compliance criteria.
Inadequate Supplier Communication: Failure to communicate TAA requirements to suppliers can lead to non-compliant products entering your supply chain. Establish clear communication channels and compliance expectations with all suppliers.
Neglecting Regular Compliance Audits: Skipping regular audits to verify the TAA status of products and suppliers can lead to compliance slippages that might go unnoticed until a formal government audit occurs.
Underestimating Penalties for Non-Compliance: Underestimating the implications of non-compliance can be costly. Penalties can include fines, exclusion from future contracts, and considerable damage to your business reputation.
By implementing these strategies and being aware of common pitfalls, businesses can ensure that their products remain compliant, safeguarding their ability to secure and fulfill federal contracts. This proactive approach mitigates risks and enhances a company’s reputation as a reliable government contractor.
Strategic Benefits and Market Opportunities for Vendors and Agencies
Compliance with the TAA opens significant vendor opportunities in the lucrative federal market. In fiscal year 2022 alone, government buyers purchased over $9 billion in products through the GSA Schedule, highlighting the scale of potential benefits. For military and law enforcement agencies, access to a diverse supplier base through GSA Schedules allows for sourcing the best ballistic-resistant materials available, combining cost-effectiveness with compliance with stringent regulations.
Are You Ready to Elevate Your Business in the Federal Marketplace?
IntelAlytic provides unmatched resources and expert guidance to help you navigate the complexities of GSA Schedules and TAA compliance. By partnering with us, you can unlock new opportunities and ensure your products meet the stringent standards required for government procurement. Discover our comprehensive suite of market resources, personalized consultations, and targeted training sessions designed to meet and exceed compliance standards. Visit IntelAlytic today to transform your approach to federal contracts and thrive in this competitive arena.
Interested in working with IntelAlytic?
Explore IntelAlytic Services
Follow us on LinkedIn for daily tips and resources